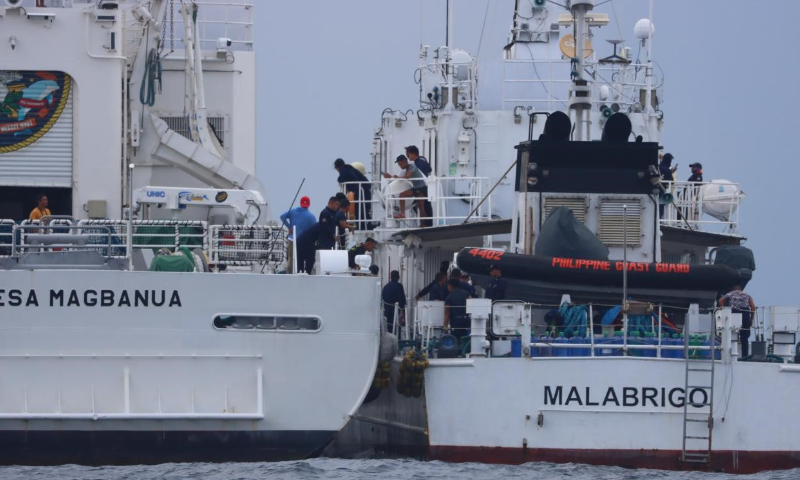
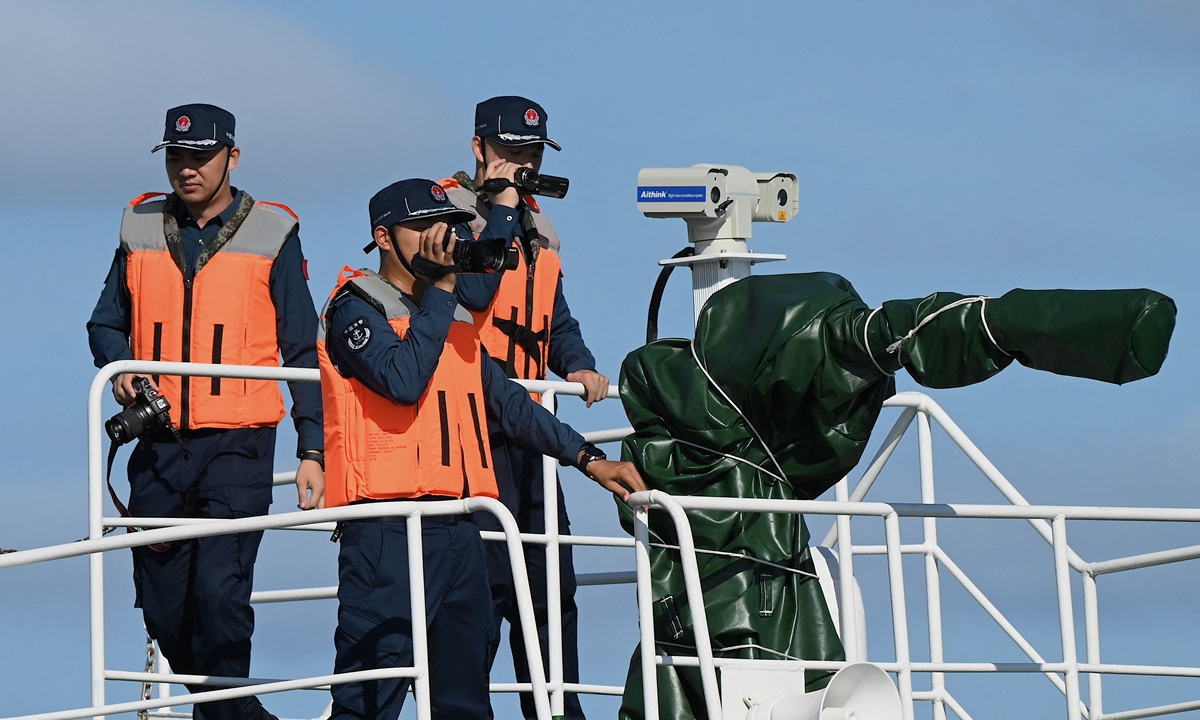
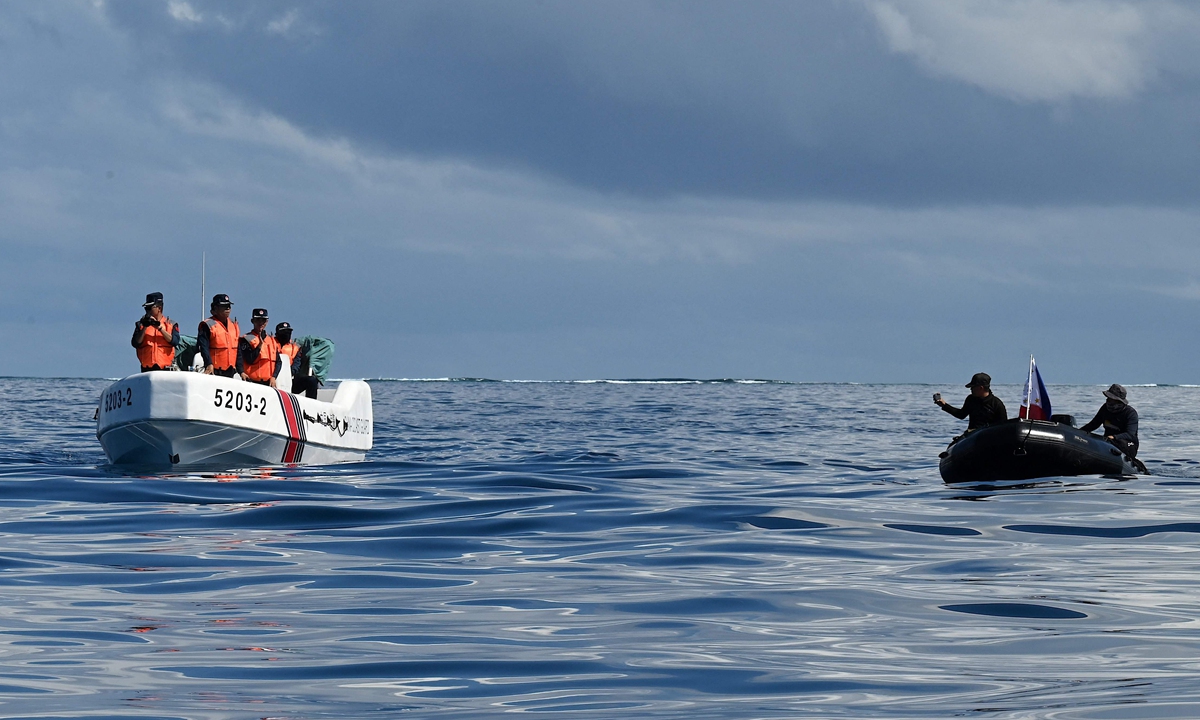
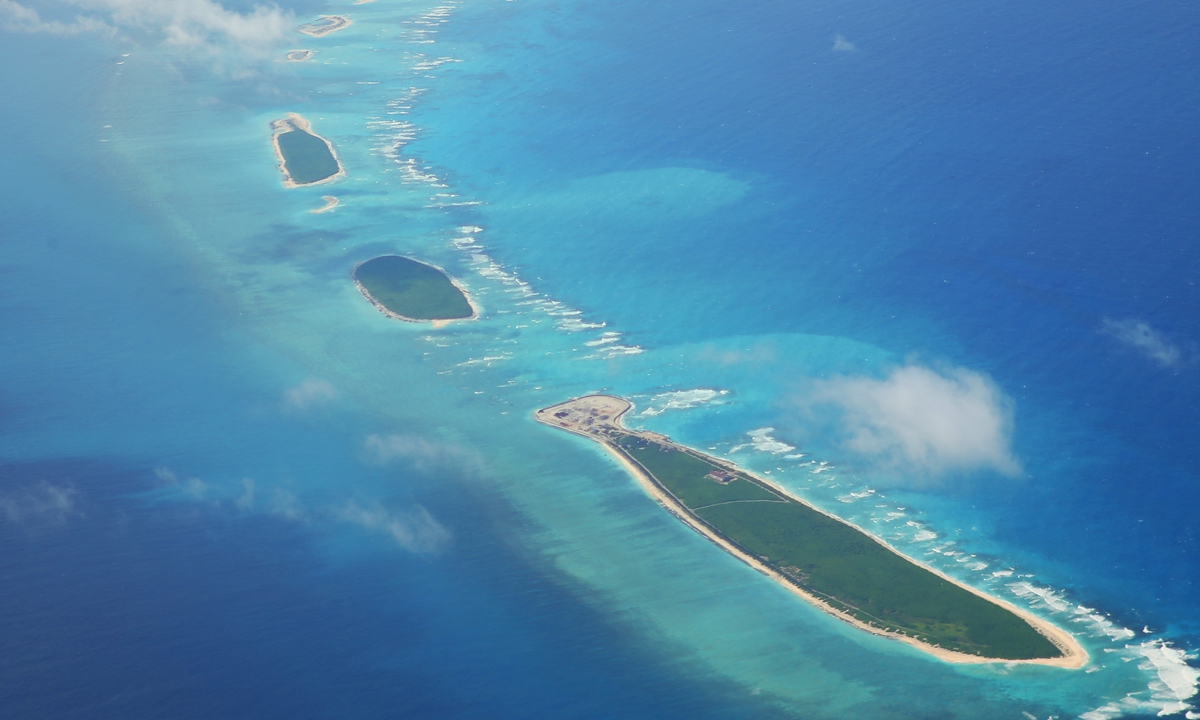
On August 26, 2024, an officer from China Coast Guard monitors Philippine Coast Guard ship 4411 which ilegally intruded into waters near China's Xianbin Jiao. Photo: China Coast Guard
It is reported that the Philippine Coast Guard ship 9701 has left Xianbin Jiao (also known as Xianbin Reef) of China's Nansha Islands, which has been illegally stationed for near five months, three days after the China-Philippine BCM meeting on the South China Sea Issue on September 11, but the Philippines did not inform the Chinese side in advance. The ship's departure shows the failure of this round of infringing provocations by the Philippines and is also a step forward in achieving peace and stability in the South China Sea.
But the Philippines and its backers will not admit defeat. How to persuade those are bent on changing the status quo in the South China Sea with infringement, and even expect to "invoke" the US-Philippines Mutual Defense Treaty to force China to give up its sovereignty and development interests, and to persuade them to recognize that China will not retreat on her sovereignty and territorial issues, is indeed a matter that requires effort and long-term patience.
First of all, it would be absurd for the Philippines to package the evacuation of BRP 9701 as a "triumphant return" after completing the "mission." To the outside world, it was obvious that the airdrop of supplies on August 28 was only a drop in the bucket, and the ship's withdrawal was more likely a helpless move after running out of supplies. Of course, the Philippines and its supporters have always been good at packaging "victory" as proof that US commitments really "work." But this is of little practical value, other than to delight a few Filipino elites and their backers.
Second, the Philippines may stick to the "misery selling" strategy, that is, hyping up China's "inhumane" obstruction of Philippine ships to resupply. However, it was in fact the BRP 9701 that invaded and forcibly stayed in the lagoon of Xianbin Jiao, and it could completely leave the lagoon on its own. The so-called need for "humanitarian supplies" is a false claim created by the Philippines. Facts have proved that the Chinese ships exercising control in the nearby waters did not stop the Philippine ship sailing away from the reef. As soon as the BRP 9701 left Xianbin Jiao, the "humanitarian crisis" was gone with it.
Finally, the Philippine side may also smear its retreat as "freedom to come and go" within its "jurisdiction." This is certainly the freedom of speech of the Philippines. Nevertheless, the struggles in recent months have demonstrated that if the Philippine side deliberately provokes and tries to force China to accept its change of the status quo in the South China Sea, it will face strong countermeasures from China. But when they choose to withdraw, China will adhere to the principle of "good to go" and not interfere. Therefore, the Philippines enjoys the freedom to respect China's sovereignty and national interests, but it does not have the freedom to make willful provocations without being stopped or countered.
It is for sure that this round of withdrawal does not mean that the Philippines will give up. Next, the Philippine Government may accuse China of still "staying" in the waters of Xianbin Jiao. But this accusation ignores the premise that China is conducting law-enforcement patrols in waters under its own jurisdiction, and without question it can stay as long as it deems necessary. Second, the withdrawal of the Philippine Coast Guard ship 9701 was done without informing China or indicating its intention to follow up. According to the latest statement of the Philippine National Maritime Commission, the BRP 9701 will still "resume its mission" after the withdrawal and completion of replenishment. Whether it intends to storm Xianbin Jiao again after repairs and supplies or send a new ship to invade, it is still worthy of caution. But for the Philippines, the lesson should be clear: Any new provocation will only invite stronger countermeasures from China, regardless of whether its next "mission" is accompanied by any warship from a third party. If the Philippines moves this kind of illegal ground sitting or illegal stay to other islands and reefs in the South China Sea, the Chinese side is also ready to shift its position and block it at any time.
It is difficult for the Philippines to succeed in illegal sitting and staying on the Chinese territory in the South China Sea, and it cannot be ruled out that the Philippines is again hyping up a "second arbitration" on the so-called environmental issue. In this regard, the Ministry of Natural Resources of China published the "A Survey Report on the Coral Reef Ecosystem of Xianbin Jiao" on August 30, elaborating on the good ecosystem status of China's Xianbin Jiao so far, and the great efforts made by China to investigate and publicize the original ecological status of Xianbin Jiao. It is precisely the illegal stay of the BRP 9701 for nearly five months that poses a real danger of pollution to the coral ecosystem of Xianbin Jiao.
In conclusion, it is a good thing that the Philippines has withdrawn the ship, and other provocations will not work. The Philippine side should take this withdrawal as a beginning of changing its South China Sea policy and shift focus onto developing pragmatic relations with China.
The author is an assistant research fellow from the Shanghai Institutes for International Studies. opinion@globaltimes.com.cn
Engagement is vital
- Chinese Coast Guard vessels fire water cannons towards a Philippine resupply vessel Unaizah May 4 on its way to a resupply mission at Seco...
Philippine conspiracy of illegally occupying Ren’ai Jiao doomed to end in failure
Re
The Philippines' despicable actions disregard the safety of its own vessel and its personnel, and disrupt peace and stability in the South China Sea.